ChaosBlade 简述及内部实现逻辑
ChaosBlade 是一款混沌工程工具,目前支持的演练场景有操作系统类的 CPU、磁盘、进程、网络,Java 应用类的 Dubbo、MySQL、Servlet 和自定义类方法延迟或抛异常等以及杀容器、杀 Pod。
Chaosblade 可直接编译运行,支持 cli 命令,具体可执行 blade create -h 查看:
Create a chaos engineering experiment
Usage:
blade create [command]
Aliases:
create, c
Examples:
create dubbo delay --time 3000 --offset 100 --service com.example.Service --consumer
Available Commands:
cplus c++ experiment
cpu Cpu experiment
disk Disk experiment
docker Execute a docker experiment
druid Druid experiment
dubbo dubbo experiment
http http experiment
jvm method
k8s Kubernetes experiment
mysql mysql experiment
network Network experiment
process Process experiment
rocketmq Rocketmq experiment,can make message send or pull delay and exception
script Script chaos experiment
servlet java servlet experiment
Flags:
-h, --help help for create
Global Flags:
-d, --debug Set client to DEBUG mode
Use "blade create [command] --help" for more information about a command.
github地址: https://github.com/chaosblade-io/chaosblade
组件架构
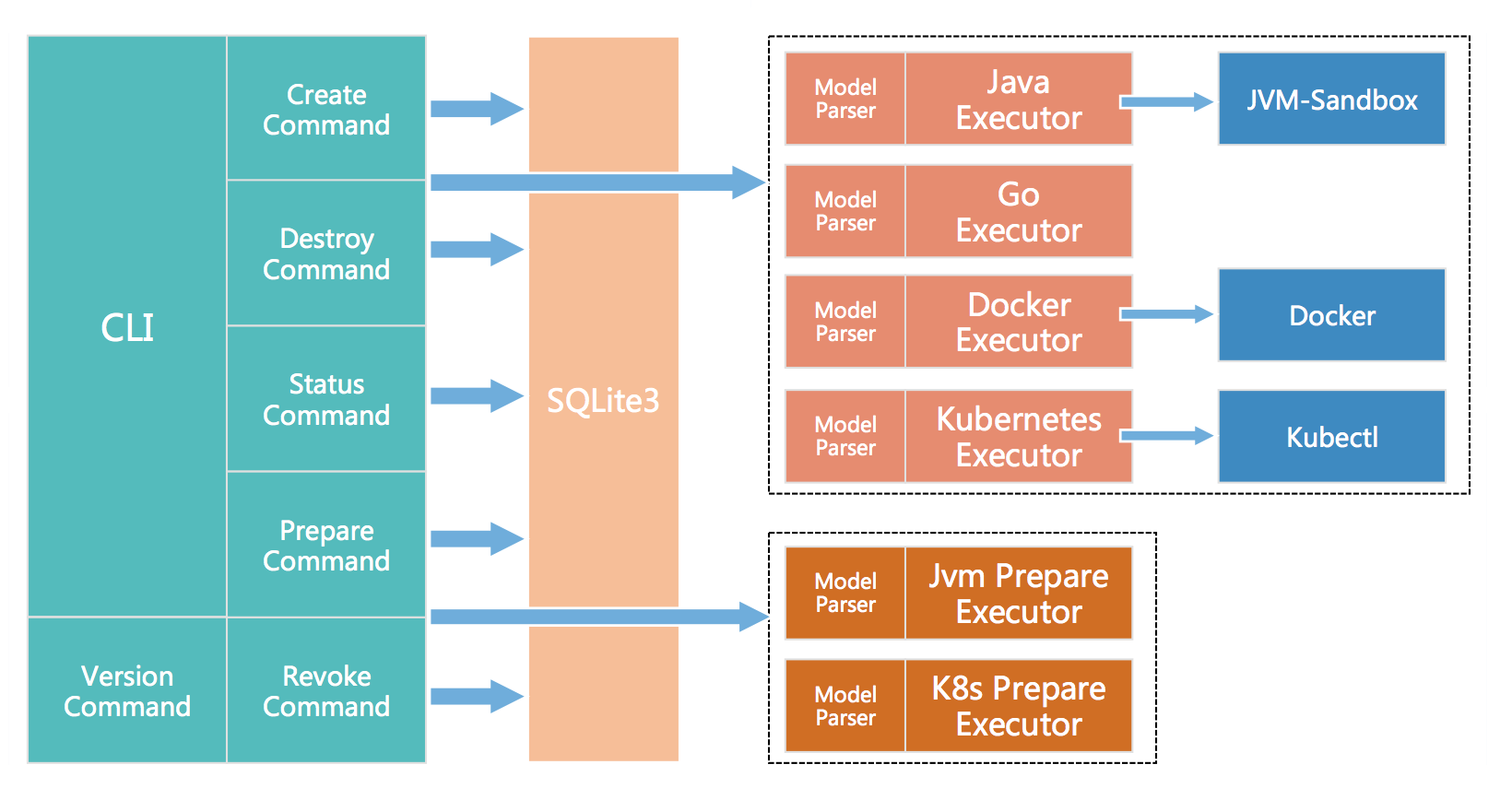
- Cli 包含 create、destroy、status、prepare、revoke、version 6 个命令;
- 相关混沌实验数据使用 SQLite 存储在本地(chaosblade 目录下);
- Create 和 destroy 命令调用相关的混沌实验执行器创建或者销毁混沌实验;
- Prepare 和 revoke 命令调用混沌实验准备执行器准备或者恢复实验环境,比如挂载 jvm-sandbox;
- 混沌实验和混沌实验环境准备记录都可以通过 status 命令查询;
ChaosBlade使用指南
获取 ChaosBlade 最新的 release 包,目前支持的平台是 linux/amd64 和 darwin/64,下载对应平台的包。
github地址: https://github.com/chaosblade-io/chaosblade/releases/
下载完成后解压即可,无需编译。解压后的目录如下:
.
├── bin
│ ├── chaos_burncpu
│ ├── chaos_burnio
│ ├── chaos_changedns
│ ├── chaos_delaynetwork
│ ├── chaos_dropnetwork
│ ├── chaos_filldisk
│ ├── chaos_killprocess
│ ├── chaos_lossnetwork
│ ├── chaos_stopprocess
│ ├── cplus-chaosblade.spec.yaml
│ ├── jvm.spec.yaml
│ └── tools.jar
├── blade
└── lib
├── cplus
│ ├── chaosblade-exec-cplus.jar
│ └── script
│ ├── shell_break_and_return_attach.sh
│ ├── shell_break_and_return.sh
│ ├── shell_check_process_duplicate.sh
│ ├── shell_check_process_id.sh
│ ├── shell_initialization.sh
│ ├── shell_modify_variable_attch.sh
│ ├── shell_modify_variable.sh
│ ├── shell_remove_process.sh
│ ├── shell_response_delay_attach.sh
│ └── shell_response_delay.sh
└── sandbox
├── bin
│ └── sandbox.sh
├── cfg
│ ├── sandbox-logback.xml
│ ├── sandbox.properties
│ └── version
├── example
│ └── sandbox-debug-module.jar
├── install-local.sh
├── lib
│ ├── sandbox-agent.jar
│ ├── sandbox-core.jar
│ └── sandbox-spy.jar
├── module
│ ├── chaosblade-java-agent-0.2.0.jar
│ └── sandbox-mgr-module.jar
└── provider
└── sandbox-mgr-provider.jar
其中 blade 是可执行文件,即 chaosblade 工具的 cli,混沌实验执行的工具。执行 ./blade help 可以查看支持命令有哪些:
$ ./blade help
An easy to use and powerful chaos engineering experiment toolkit
Usage:
blade [command]
Available Commands:
create Create a chaos engineering experiment
destroy Destroy a chaos experiment
help Help about any command
prepare Prepare to experiment
query Query the parameter values required for chaos experiments
revoke Undo chaos engineering experiment preparation
status Query preparation stage or experiment status
version Print version info
Flags:
-d, --debug Set client to DEBUG mode
-h, --help help for blade
Use "blade [command] --help" for more information about a command.
blade 命令列表如下:
- prepare:简写 p,混沌实验前的准备,比如演练 Java 应用,则需要挂载 java agent。要演练应用名是 business 的应用,则在目标主机上执行 blade p jvm –process business。如果挂载成功,返回挂载的 uid,用于状态查询或者撤销挂载使用;
- revoke:简写 r,撤销之前混沌实验准备,比如卸载 java agent。命令是 blade revoke UID;
- create: 简写是 c,创建一个混沌演练实验,指执行故障注入。命令是 blade create [TARGET] [ACTION] [FLAGS],如果注入成功,则返回实验的 uid,用于状态查询和销毁此实验使用;
- destroy:简写是 d,销毁之前的混沌实验,比如销毁上面提到的 Dubbo 延迟实验,命令是 blade destroy UID;
- status:简写 s,查询准备阶段或者实验的状态,命令是 blade status UID 或者 blade status –type create;
以上命令帮助均可使用 blade help [COMMAND]。
应用示例
以CPU使用率100%的故障为例,即blade create cpu fullload命令。blade create cpu的用法如下:
$ ./blade create cpu -h
Cpu experiment, for example full load
Usage:
blade create cpu [flags]
blade create cpu [command]
Examples:
cpu fullload
Available Commands:
fullload cpu fullload
Flags:
--cpu-count string Cpu count
--cpu-list string CPUs in which to allow burning (0-3 or 1,3)
-h, --help help for cpu
Global Flags:
-d, --debug Set client to DEBUG mode
Use "blade create cpu [command] --help" for more information about a command.
执行实验:
$ ./blade create cpu fullload
{"code":200,"success":true,"result":"d9e3879cb68416a2"}
注意上面的result: d9e3879cb68416a2中的d9e3879cb68416a2,这个在停止实验的时候会用到(./blade destroy UID)。
采用iostat -c 1 1000命令查看CPU使用率(%idle):
avg-cpu: %user %nice %system %iowait %steal %idle
98.75 0.00 1.25 0.00 0.00 0.00
查看CPU的使用率还可以使用sar命令、top命令等。
此时命令已经生效。下一步停止实验,执行:
$ ./blade destroy d9e3879cb68416a2
{"code":200,"success":true,"result":"command: cpu fullload --debug false --help false"}
再观察CPU的情况,负载已经回到正常状态:
avg-cpu: %user %nice %system %iowait %steal %idle
0.25 0.00 0.50 2.00 0.00 97.25
ChaosBlade 内部实现逻辑简述
以cpu满载(使用率达到100%)举例。在./blade create cpu命令中,我们可以通过--cpu-count用来指定cpu满载的内核个数;还可以通过--cpu-list来指定需要的满载的cpu内核编号,可以使用“1,3”这种形式来分别指定编号为1和3的cpu内核满载,也可以“0-3”这种形式来指定编号为0至3(0,1,2,3)的cpu内核满载。
逻辑剖析
如果不是直接使用下载的release版本,而是使用源码。那么在使用 ChaosBlade 前需要将源码(project)编译,其中就会把project下的 exec/os/bin/ 目录下的文件编译成chaos_xxx类型的可执行文件。
exec/os/bin/目录内容如下:
$ cd exec/os/bin/
$ tree
.
├── burncpu
│ ├── burncpu.go
│ └── burncpu_test.go
├── burnio
│ ├── burnio.go
│ └── burnio_test.go
├── changedns
│ ├── changedns.go
│ └── changedns_test.go
├── common.go
├── delaynetwork
│ ├── delaynetwork.go
│ └── delaynetwork_test.go
├── dropnetwork
│ ├── dropnetwork.go
│ └── dropnetwork_test.go
├── filldisk
│ ├── filldisk.go
│ └── filldisk_test.go
├── killprocess
│ ├── killprocess.go
│ └── killProcess_test.go
├── lossnetwork
│ ├── lossnetwork.go
│ └── lossnetwork_test.go
└── stopprocess
└── stopprocess.go
在使用./blade create cpu fulloload命令的时候其实在内部就转化为了直接调用 bin/chaos_burncpu。而blade这个可执行文件只是使用了Cobra来实现的CLI入口。
Cobra既是用于创建强大的现代CLI应用程序的库,也是用于生成应用程序和命令文件的程序。许多使用最广泛的Go项目都是使用Cobra构建的,其中包括:kubernetes、docker、openshift、Hugo等。
也就是说,实际上我们不需要使用./blade create cpu fulloload命令来使得cpu满载,使用bin/目录下的chaos_burncpu即可。
burncpu实现简述
chaos_burncpu中实现CPU满载负荷的逻辑其实相当简单,通过程序让CPU一直运作即可。代码如下:
func burnCpu() {
runtime.GOMAXPROCS(cpuCount)
for i := 0; i < cpuCount; i++ {
go func() {
for {
for i := 0; i < 2147483647; i++ {
}
runtime.Gosched() //让出CPU时间片
}
}()
}
select {} // wait forever
}
关闭CPU满载负荷的过程也比较简单粗暴,总共分为两步:
- 使用
ps -ef | grep …命令找出chaos_burncpu的pid。 - 使用
kill -9 pid命令干掉它。
指定内核满载
我们在上面就了解到通过--cpu-count可以指定CPU满载的内核个数,通过--cpu-list可以指定内核满载。
--cpu-count的功能很好实现,在上面的func burnCpu()函数中的cpuCount就是--cpu-count所指定的值。
--cpu-list的功能比较复杂,总共分为3步:
- 第一步:执行
nohup bin/chaos_burncpu --nohup --cpu-count 1 --cpu-processor [cpu内核编号] > /dev/null 2>&1 &。假设我们要指定编号为1的内核满载,那么对应的命令即为:nohup bin/chaos_burncpu --nohup --cpu-count 1 --cpu-processor 1 > /dev/null 2>&1 &。其实这个只是个烟雾弹,实际上还是调用原本的bin/chaos_burncpu --start --cpu-count 1而已,只不过这里多了一个 cpu-processor 的信息,这个在下面有用。 - 第二步:执行
ps -ef | grep …命令找出对应的pid。 - 第三步:将进程pid绑定到编号为 cpu-processor 的内核上。
CPU affinity (亲和力/亲和性)是一种调度属性(scheduler property), 它可以将一个进程"绑定" 到一个或一组CPU上。taskset命令用于获取或者设定CPU affinity。
OS级故障实现原理解析
在上一章中我们了解了burncpu的故障实现原理,本章主要来描述一下下面列表中除burncpu之外的故障实现原理。
├── bin
│ ├── chaos_burncpu
│ ├── chaos_burnio
│ ├── chaos_changedns
│ ├── chaos_delaynetwork
│ ├── chaos_dropnetwork
│ ├── chaos_filldisk
│ ├── chaos_killprocess
│ ├── chaos_lossnetwork
│ ├── chaos_stopprocess
1. chaos_burnio
模拟I/O读写满负荷运作:
bin/chaos_burnio --file-system /dev/sda1 --size 1 --count 1024 --read=true --write=false --nohup=true
bin/chaos_burnio --file-system /dev/sda1 --size 1 --count 1024 --read=false --write=true --nohup=true
原理:
# read
dd if=/dev/sda1 of=/dev/null bs=1M count=1024 iflag=dsync,direct,fullblock
# write
dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/chaos_burnio.log.dat bs=1M count=1024 oflag=dsync
2. chaos_filldisk
磁盘填充:
# 其中size是指定填充磁盘的大小,单位为MB
./blade create disk fill --size 1000
原理:
dd if=/dev/zero of=/chaos_filldisk.log.dat bs=1M count=1000 iflag=fullblock
3. chaos_changedns
域名设定:
./blade create network dns --domain www.hidden.com --ip localhost
实际效果会在/etc/hosts中添加一行记录:
localhost www.hidden.com #claosblade
反之,就是删除掉这一行。
4. chaos_delaynetwork
网络延迟:
# time指定延迟时间,单位为ms, offset指定延迟波动大小
./blade create network delay --interface eth0 --time 300
./blade create network delay --interface eth0 --time 300 --offset 50
原理:
tc qdisc add dev eth0 root netem delay 300ms
#该命令将 eth0 网卡的传输设置为延迟 300ms ± 50ms (250 ~ 350 ms 之间的任意值)发送
tc qdisc add dev eth0 root netem delay 300ms 50ms
恢复:
tc qdisc del dev eth0 root netem
5. chaos_dropnetwork
网络中断:
./blade create network drop --local-port 100 --remote-port 100
原理:
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport [localPort] -j DROP
iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport [localPort] -J DROP
iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --dport [remotePort] -j DROP
iptables -A OUTPUT -p udp --dport [remotePort] -j DROP
恢复:
iptables -D INPUT -p tcp --dport [localPort] -j DROP
iptables -D INPUT -p udp --dport [localPort] -J DROP
iptables -D OUTPUT -p tcp --dport [remotePort] -j DROP
iptables -D OUTPUT -p udp --dport [remotePort] -j DROP
6. chaos_lossnetwork
网络丢包:
./blade create network loss --interface eth0 --percent 10
原理:
tc qdisc add dev eth0 root netem loss 10%
7. chaos_killprocess
杀死进程:
./blade create process kill --process chaos
原理:
kill -9
8. chaos_stopprocess
进程假死:
./blade create process stop --process chaos
原理:
kill -19
# 恢复:kill -18
附录:各种信号及其用途。
$ kill -l
1) SIGHUP 2) SIGINT 3) SIGQUIT 4) SIGILL 5) SIGTRAP
6) SIGABRT 7) SIGBUS 8) SIGFPE 9) SIGKILL 10) SIGUSR1
11) SIGSEGV 12) SIGUSR2 13) SIGPIPE 14) SIGALRM 15) SIGTERM
16) SIGSTKFLT 17) SIGCHLD 18) SIGCONT 19) SIGSTOP 20) SIGTSTP
21) SIGTTIN 22) SIGTTOU 23) SIGURG 24) SIGXCPU 25) SIGXFSZ
26) SIGVTALRM 27) SIGPROF 28) SIGWINCH 29) SIGIO 30) SIGPWR
31) SIGSYS 34) SIGRTMIN 35) SIGRTMIN+1 36) SIGRTMIN+2 37) SIGRTMIN+3
38) SIGRTMIN+4 39) SIGRTMIN+5 40) SIGRTMIN+6 41) SIGRTMIN+7 42) SIGRTMIN+8
43) SIGRTMIN+9 44) SIGRTMIN+10 45) SIGRTMIN+11 46) SIGRTMIN+12 47) SIGRTMIN+13
48) SIGRTMIN+14 49) SIGRTMIN+15 50) SIGRTMAX-14 51) SIGRTMAX-13 52) SIGRTMAX-12
53) SIGRTMAX-11 54) SIGRTMAX-10 55) SIGRTMAX-9 56) SIGRTMAX-8 57) SIGRTMAX-7
58) SIGRTMAX-6 59) SIGRTMAX-5 60) SIGRTMAX-4 61) SIGRTMAX-3 62) SIGRTMAX-2
63) SIGRTMAX-1 64) SIGRTMAX